Difference between revisions of "Disability/Employment"
Matthewljw (talk | contribs) |
Matthewljw (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== '''EMPLOYMENT''' == | == '''EMPLOYMENT''' == | ||
| − | + | [[File:ToC.png|thumb|918x918px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | ==== ''' | + | ==== '''Engaging and Equipping Employers''' ==== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==== Need for ready supply of jobs ==== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==== Need for ready supply of jobs | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|Ready supply of jobs | |Ready supply of jobs | ||
| Line 264: | Line 79: | ||
#* Purposeful job reservation – quota hiring system or protected industries (e.g., horticulture/farming at HDB veg plots, postal/mail distribution, food preparation, wholesale veg processing, carwashing, logistics. Can parents be funded to set up viable businesses to train/support their SNCs? | #* Purposeful job reservation – quota hiring system or protected industries (e.g., horticulture/farming at HDB veg plots, postal/mail distribution, food preparation, wholesale veg processing, carwashing, logistics. Can parents be funded to set up viable businesses to train/support their SNCs? | ||
#* Carrots – tax incentives/rebates, educate businesses on schemes (e.g., ODP) | #* Carrots – tax incentives/rebates, educate businesses on schemes (e.g., ODP) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | ==== Need for secure jobs | + | ==== Need for secure jobs ==== |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|Available Information | |Available Information | ||
| Line 430: | Line 151: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | ==== Need for inclusive workplace | + | ==== Need for inclusive workplace ==== |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|Definition | |Definition | ||
| Line 437: | Line 158: | ||
* Appropriate and reasonable re-design/modifications/accommodations to workplace and job are made | * Appropriate and reasonable re-design/modifications/accommodations to workplace and job are made | ||
* Attitudinal barriers at workplace are absent | * Attitudinal barriers at workplace are absent | ||
| + | Inclusive workplaces should include | ||
| + | * Fair recruitment and procurement practices | ||
| + | * Policies concerning equality and human rights, working conditions, dignity at work, employee welfare | ||
| + | * Reasonable accommodation made by employers: | ||
| + | ** An accommodation is defined as any change in work environment or processes to allow an employee with disability to enjoy equal employment opportunities. | ||
| + | * A welcoming workplace culture | ||
| + | ** “Inclusion goes beyond merely having a mix of employees with different demographics and backgrounds in the workplace. It is about appreciating employees for the unique value they bring to the workplace, and leveraging on those differences to add value to the organisation so that both the person and the organisation can flourish.”<ref>https://www.tafep.sg/sites/default/files/E-News%20April%202011_files/Publication%20CIW%20Start%20Up%20Kit%20(as%20of%20040712).pdf</ref> | ||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 491: | Line 219: | ||
* Disabled People’s Association (DPA) 2015 study “Achieving Inclusion in the Workplace” | * Disabled People’s Association (DPA) 2015 study “Achieving Inclusion in the Workplace” | ||
* DPA-IPS 2016-2017 participatory research “Employment Discrimination Against People with Disabilities” | * DPA-IPS 2016-2017 participatory research “Employment Discrimination Against People with Disabilities” | ||
| + | Gaps | ||
| + | # Inclusive workplaces are rare in Singapore, where persons with disabilities (PWDs) comprise just 0.55 per cent of the resident labour force. They are mainly employed in the hospitality, food and beverage, wholesale and retail, and administrative support sectors"<ref>https://www.straitstimes.com/lifestyle/myth-of-the-disabled-worker</ref> | ||
Questions | Questions | ||
# Do official HR curricula (e.g. SHRI) teach on how to support companies to employ PWDs fairly? | # Do official HR curricula (e.g. SHRI) teach on how to support companies to employ PWDs fairly? | ||
| Line 499: | Line 229: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | ==== Need for continued opportunities for job growth, career development and skills upgrading | + | ==== '''Job Matching/Placement''' ==== |
| + | |||
| + | ==== Need for information on available job opportunities for persons with disabilities ==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |To know about job opportunities | ||
| + | * Focus is on knowledge and awareness (of job opportunities) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | !EXISTING RESOURCES | ||
| + | !GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | ||
| + | !POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://employment.sgenable.sg/jobseekers/employment-assistance/ SG Enable - Job Advisory] | ||
| + | * Job-readiness assessment by specialists such as occupational therapists/psychologists/employment coaches. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://eservice1.enable.gov.sg/MSFPortal/EDS/Employment/Pages/Common/Index/Index.aspx SG Enable — Disability Employment Jobs Portal] | ||
| + | * Job portal for PwDs to search for opportunities | ||
| + | |Jobs listed on most job portals do not reflect if the hiring company is interested to employ PWDs. Career events are not always universally designed as well. | ||
| + | |Employers can reflect if they are keen to employ PWDs, at career events, on job portals and other avenues. | ||
| + | Having a “ready-to-hire PWDs” mark would ease PWDs’ job search process. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://able-sg.org/return_to_work.html ABLE Return to Work Programme] | ||
| + | * Provides physical rehabilitation, vocational rehabilitation, social support, training, return-to-work coordination and employment support | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.bizlink.org.sg/services/vocational-assessment-program/ BizLink Vocational Assessment Service] | ||
| + | * Provides assessment for a disabled individual to determine strengths and weaknesses pertaining to work capacity | ||
| + | * Assist people with disabilities and/or special needs in exploring job opportunities and training | ||
| + | * Offer assistance and counselling to PWDs and/or their families on issues relating to disabilities or work-related issues | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.spd.org.sg/employment-support-programme/ SPD Employment Support Programme (ESP)] | ||
| + | * Vocational training and employment planning for persons with permanent disabilities 16 years and above | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.spd.org.sg/transition-to-employment/ SPD Transition To Employment Programme (TTE)] | ||
| + | * Aims to reintegrate people with acquired physical disabilities aged 18-60 back into the workforce | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.autism.org.sg/core-services/e2c#tab_e2cProgramme ARC Employability & Employment Centre (E2C) Programme] | ||
| + | * Autism-specific pre-assessment, assessment, employability training, job placement and job support | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.minds.org.sg/AdultSvcs.html#EDCprogramme MINDS Employment Development Centres (EDCs)] | ||
| + | Provides vocational training for adults with intellectual disabilities aged 18 and above: | ||
| + | * [http://www.minds.org.sg/IEDC/index.html Idea Employment Development Centre] | ||
| + | * [http://www.minds.org.sg/SMEDC/ SIA-MINDS Employment Development Centre] | ||
| + | * [http://www.minds.org.sg/WEDC/ Woodlands Employment Development Centre] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="3" |Gaps | ||
| + | # In helping PWDs find a variety of suitable job opportunities, VWOs and SPED schools still need to take initiative to make connections themselves, or rely on personal contacts. SPED graduates tend to lack information on job opportunities beyond their track – type, pay range, skillsets required etc. | ||
| + | #* An ex-student who worked in Coffee Bean switched to forklift driving after finding out on his own that the latter paid better | ||
| + | Questions | ||
| + | # Are there other organisations apart from SPD, ABLE and SG Enable that provides job support and placement services to persons with acquired disabilities (e.g., stroke survivors, traumatic brain injury)? | ||
| + | # For the planned 2020 disability census, can we find out how many people have acquired disabilities, and have the data split by disability types? Related question – do we know why SGE’s definition of disability does not cover temporary disabilities? | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''Continuing Career Development''' ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Need for continued opportunities for job growth, career development and skills upgrading ==== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!EXISTING RESOURCES | !EXISTING RESOURCES | ||
| Line 534: | Line 333: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | ==== Need for financial independence and stability | + | ==== Need for financial independence and stability ==== |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!EXISTING RESOURCES | !EXISTING RESOURCES | ||
| Line 549: | Line 348: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''PWD Training & Work Readiness''' ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Need to be job ready ==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |How 'job ready' is understood | ||
| + | * To obtain vocational/technical, soft and employability skills | ||
| + | * To be aware of their own strengths and preferences | ||
| + | * For those with acquired disabilities: To be in good psychosocial health, mindset and adjusted expectations | ||
| + | * To be proactive in searching for jobs | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | !EXISTING RESOURCES | ||
| + | !GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | ||
| + | !POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.skillsfuture.sg/ SkillsFuture] | ||
| + | * All Singaporeans aged 25 and above have S$500 in credit to take courses[[Disability#cite note-57|[57]]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Vocational Training in SPED Schools | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://employment.sgenable.sg/students/special-education-students School-to-Work Transition Programme (S2W)] | ||
| + | * Begins in the year of graduation and lasts for up to a year after | ||
| + | * Students with the potential to work identified by SG Enable and schools and matched to job training | ||
| + | * 24 in 30 students who joined S2W found a job, with 20 remaining employed for at least 6 months[[Disability#cite note-58|[58]]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | * EM3 has taken note of this: To scale up S2W programme so that more SPED school students can participate[[Disability#cite note-:12-3|[3]]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | rowspan="3" |[https://www.moe.gov.sg/education/special-education/special-education-schools/sped-curriculum-framework#Vocational-Education-in-SPED-School Framework for Vocational Education] | ||
| + | To guide the 19 SPED schools in designing a structured vocational education programme that includes vocational guidance, an assessment of students’ interests, preferences and strengths, and opportunities for structured and authentic work experiences to support development of work habits and skills. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Enabling Masterplan 3[[Disability#cite note-59|[59]]] | ||
| + | * MOE to work more closely with SPED schools to further strengthen vocational preparation for SPED students | ||
| + | * SG Enable, MSF and MOE to work with the community to strengthen and expand opportunities for vocational training and job placements | ||
| + | |Some SPED students have difficulty mastering job skills training even when approaching graduation/18 years old. Can they continue learning even after graduation? | ||
| + | |Allow SPED students to attend courses ad-hoc, even after graduation. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |SPED school graduates lack internship opportunities during their school-going years and a foothold in permanent employment. SPED schools and VWOs typically do this through their own contacts. | ||
| + | |Have a central coordinator that facilitates the internship process. What are the possible alternatives for students who are unsuccessful in an internship placement? | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Content taught in WSQ- and WPLN- certified courses may not always be understood, and skills learnt not retained and applied. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Transition Planning Guide | ||
| + | (entitled Transition Planning For Living, Learning And Working - Making It Happen) | ||
| + | * Received by all SPED schools in 2017 | ||
| + | * For SPED schools to help students with setting post-school goals; provides suggestions and templates on how schools and parents can prepare students for the transition process[[Disability#cite note-60|[60]]] | ||
| + | |Question: Are there channels available for teachers and parents to provide feedback on the transition planning process? | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.mettaschool.edu.sg/programmes/vocational-programme/ Metta School’s Vocational Certification Programme] | ||
| + | Institute of Technical Education Skills Certificate (ISC) | ||
| + | * For eligible students 17 years old and above | ||
| + | * Offers ITE Skills Certification (ISC) upon completion, e.g., in Baking, Food Preparation and Housekeeping Operation (Accommodation) | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.mettaschool.edu.sg/programmes/employment-pathway-programme/ Metta School’s Employment Pathway Programme (EPP)] | ||
| + | * For MID and ASD programme students not on the Vocational Certification track | ||
| + | * Students will undergo vocational skills training, such as WSQ modules, Food and Hygiene courses, etc. and job trials and on-the-job training | ||
| + | * Upon graduation, SG Enable will support these students with vocational training and support in identified suitable pathways such as supported employment, customized employment and internships. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.mettaschool.edu.sg/programmes/c-programme/ Metta School’s C (Career) Programme] | ||
| + | * For MID students between 13 and 16, preparing them for vocational skills training and/or employment | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.apsn.org.sg/schools/delta-senior-school/programmes/ APSN Delta Senior School’s Vocational Certification Programme] - Singapore Workforce Skills Qualifications (WSQ) | ||
| + | * For students aged 17 to 21, in four areas: (1) Food Services; (2) Hotel and Accommodation Services; (3) Landscape Operations and (4) Retail Operations. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="3" |Students in Institutes of Higher Learning (IHL) – Universities or Polytechnics | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://employment.sgenable.sg/students/internship-programme IHL Internship Programme] | ||
| + | * Provides internship opportunities for IH students with ASD, ID, PI and SI | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://employment.sgenable.sg/students/rise-mentorship-programme Rise Mentorship Programme] | ||
| + | * 12-week programme where students are matched with business managers who provide mentoring in job interviews, resume writing skills etc. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="3" |Non-Students/Adults with Disabilities | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Vocational Training | ||
| + | For post-primary school students, available at: | ||
| + | * [https://savh.org.sg/ Singapore Association of the Visually Handicapped (SAVH)] | ||
| + | * [http://sadeaf.org.sg/ Singapore Association for the Deaf (SADeaf) – Mountbatten Vocational School] | ||
| + | * [https://www.autismlinks.org.sg/programmes/ecfa Autism Association (Singapore) – Eden Centre for Adults] | ||
| + | * [http://cpas.org.sg/our-programmes/pro-grow/key-programmes/ Cerebral Palsy Alliance Singapore – Goodwill, Rehabilitation and Occupational Workshop (GROW)] | ||
| + | * [http://downsyndrome-singapore.org/post/view/8/23 Down Syndrome Association – Adult Enhancement Programme] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.bizlink.org.sg/services/vocational-assessment-program/ BizLink Vocational Assessment Service] | ||
| + | * Provides assessment to determine strengths and weaknesses in areas related to work capacity, exploration of job opportunities/training in social enterprises or Bizlink sheltered workshops, and disability-relation counselling/assistance. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://employment.sgenable.sg/students/cv-clinic/ CV Clinics by Singapore Business Network on Disability] | ||
| + | * Business professionals provide CV/resume and interview advice, graduates with disabilities share experiences from their career journeys | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://employment.sgenable.sg/jobseekers/get-trained/ Training Programmes] | ||
| + | * Wide selection of courses to develop vocational skills | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.able-sg.org/rehab.html ABLE Return-to-Work Programme] | ||
| + | * Provides physical rehabilitation, vocational rehabilitation, social support, training, return-to-work coordination and employment support. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://employment.sgenable.sg/jobseekers/hospital-to-work-programme/ Hospital-to-Work Programme] | ||
| + | * Provides persons with acquired disabilities with support and opportunities to overcome the challenges in gaining sustainable employment. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.spd.org.sg/employment-support-programme/ SPD Employment Support Programme (ESP)] | ||
| + | * Vocational training and employment planning for persons with permanent disabilities 16 years and above | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.spd.org.sg/transition-to-employment/ SPD Transition To Employment Programme (TTE)] | ||
| + | * Aims to reintegrate people with acquired physical disabilities aged 18-60 back into the workforce | ||
| + | |Job coaches face difficulties in providing psychosocial support for those with acquired disabilities. Some PWDs have difficulty accepting their disabilities and the job coaches are not trained to provide psychosocial support to address these issues. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.autism.org.sg/core-services/e2c#tab_e2cProgramme Employability & Employment Centre (E2C) Programme] | ||
| + | * Autism-specific pre-assessment, assessment, employability training, job placement and job support | ||
| + | |An individual with autism received vocational assistance from ARC; he paid $494 (after subsidy) for the vocational assessment but was deemed unemployable. However, he managed to secure a job later through his & his family’s efforts with Dignity Kitchen. | ||
| + | * ARC has responded to this. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[http://www.minds.org.sg/AdultSvcs.html#EDCprogramme MINDS Employment Development Centres (EDCs)] | ||
| + | Provides vocational training for adults with intellectual disabilities aged 18 and above: | ||
| + | * [http://www.minds.org.sg/IEDC/index.html Idea Employment Development Centre] | ||
| + | * [http://www.minds.org.sg/SMEDC/ SIA-MINDS Employment Development Centre] | ||
| + | * [http://www.minds.org.sg/WEDC/ Woodlands Employment Development Centre] | ||
| + | * Minds regularly organises internships in industries as diverse as laundromats, supermarkets, hardware shops and car wash facilities in petrol stations for its clients starting from the age of about 16. By around age 19, some PWDs can be guided towards working in sheltered workshops that cater to them, doing work such as packing, retail, baking and making crafts. Others are placed in the general labour market, where they are mentored and supported by job coaches from Minds who ensure that they are not stressed in their new environment or check that they are able to take public transport to work.<ref>https://www.straitstimes.com/lifestyle/myth-of-the-disabled-worker</ref> | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[https://www.sgenable.sg/pages/content.aspx?path=/for-adults/sheltered-workshops/ Sheltered Workshops] | ||
| + | * Offers employment or vocational training to adults with disabilities who do not possess the competencies or skills for open employment, allowing them to practice in jobs or tasks where the processes are either simple or broken down into simpler steps. | ||
| + | * 8 workshops as of 13 August 2018 | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan="3" |Gaps | ||
| + | # PWDs’ employability may be at risk in view of increasing automation and technological advancement. Can we equip them to work alongside technologies such as digital media, handheld tech, machines? Is there a group that needs support most? | ||
| + | #* To consult/learn from Orana, Australia in this respect | ||
| + | # There is a lack of information on trends and relevance of industries that SPED schools usually train their students to enter. How are these industries projected to change? Will there be sufficient job opportunities available? | ||
| + | Questions | ||
| + | # To study European apprenticeship models to improve on vocational training and transition planning? Other countries? | ||
| + | # Are vocational assessments of strengths, job preferences and skills accessible and effective? | ||
| + | # Is there available statistical data on the number of SPED students who have: | ||
| + | #* Secured jobs (private / public sector) or | ||
| + | #* Are enrolled in organisations for further job training (sheltered workshop) immediately after graduation? | ||
| + | #* Is there data that informs us of how these numbers change over the years? | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 09:44, 4 June 2019
Contents
- 1 EMPLOYMENT
- 1.1 Engaging and Equipping Employers
- 1.2 Need for ready supply of jobs
- 1.3 Need for secure jobs
- 1.4 Need for inclusive workplace
- 1.5 Job Matching/Placement
- 1.6 Need for information on available job opportunities for persons with disabilities
- 1.7 Continuing Career Development
- 1.8 Need for continued opportunities for job growth, career development and skills upgrading
- 1.9 Need for financial independence and stability
- 1.10 PWD Training & Work Readiness
- 1.11 Need to be job ready
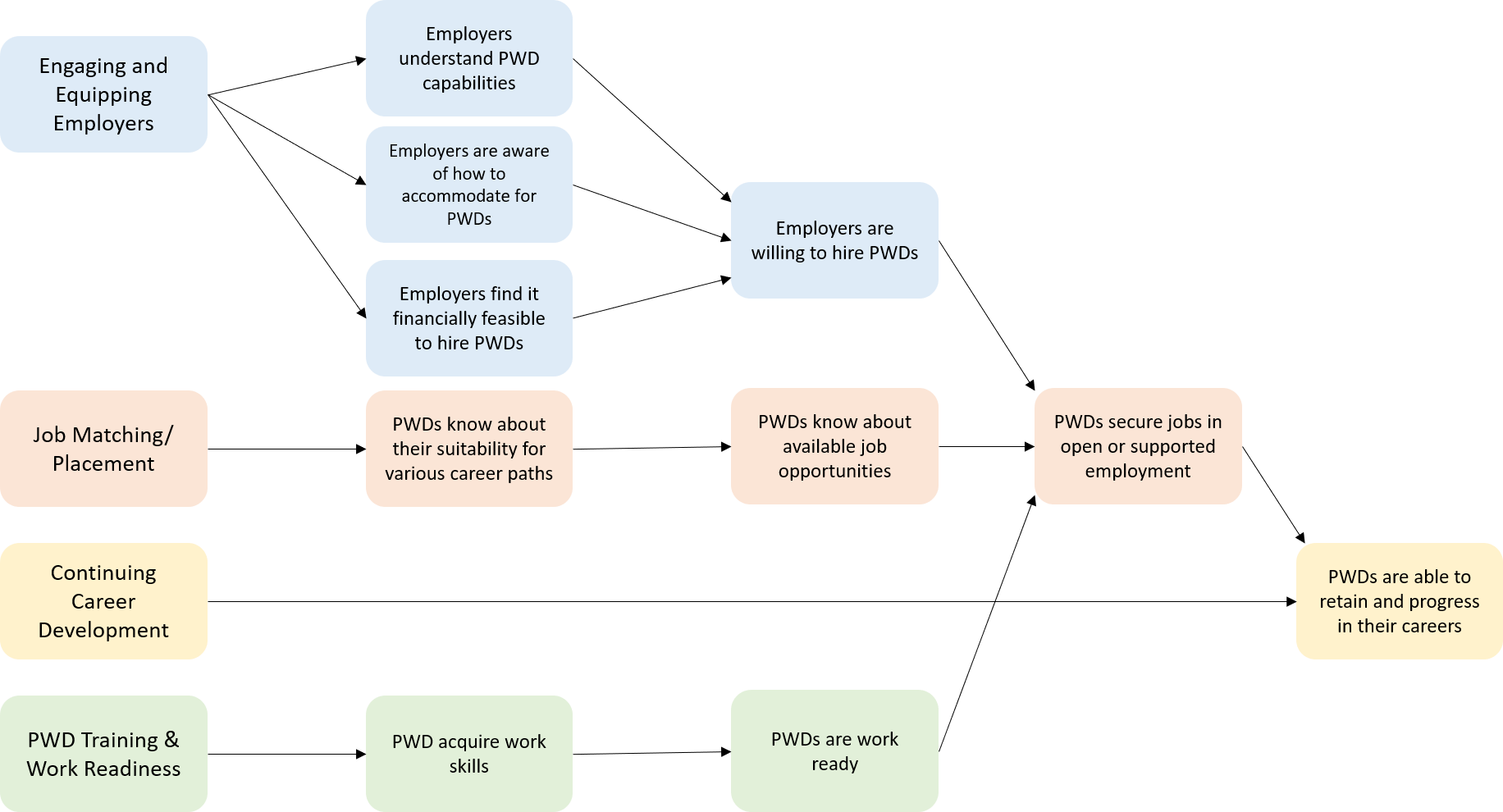
EMPLOYMENT
Engaging and Equipping Employers
Need for ready supply of jobs
Ready supply of jobs
|
| EXISTING RESOURCES | GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|
Inclusive Business Forum (IBF) and “Fostering Inclusion At The Workplace” Seminar
|
Can there be more opportunities to dialogue with employers or partners such as WSG/MOM, such that the process may be more institutionalised/supported? | |
Special Employment Credit (SEC)
|
||
| Government efforts to set up employment centres in residential neighbourhoods | Question: Any updates on the neighbourhood employment centres? | |
| Employment Opportunities | ||
Inclusive Employers in Singapore
|
||
Sheltered Workshops
|
Some PWDs may find sheltered employment too easy/not challenging, yet be unsuited for open employment. What of a supported employment model?
|
|
Public Service Career Placement (PSCP) Programme
|
||
Gaps
Questions
| ||
Need for secure jobs
Available Information
|
| EXISTING RESOURCES | GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|
School-to-work transition programme (S2W)
|
||
SPD Employment Support Programme (ESP)
|
Job retention is a major issue even if people with disabilities are hired. | Consider to improve rapport between employers and job support and placement agencies (JPJS), to increase the likelihood of employers approaching JPJS agencies and being more forthcoming whenever they face issues (e.g. behavioural) with PWD employees that are new on-board. SPD provides job coaching support post-employment for up to six months. |
SPD Transition To Employment Programme (TTE)
|
||
ARC Employability & Employment Centre (E2C) Programme
|
||
| MINDS Employment Development Centres (EDCs)
Provides vocational training for adults with intellectual disabilities aged 18 and above: |
||
ABLE Return-to-Work Programme
|
||
Public Service Career Placement (PSCP) Programme
|
||
Gaps
Questions
| ||
Need for inclusive workplace
Definition
Inclusive workplaces should include
|
| EXISTING RESOURCES | GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|
Open Door Programme
|
||
Guidelines by Tripartite Alliance for Fair and Progressive Employment Practices (TAFEP) for fair employment practices
|
||
Inclusive Business Forum (IBF) and “Fostering Inclusion At The Workplace” Seminar
|
||
Enabling Employers Network
|
||
Singapore Business Network on Disability
|
||
SG Enable employer resources
|
||
| DPA Diversity Inclusion Workshops | ||
Disability education training for employers and co-workers of PWDs
|
||
Experiences of PWDs in the workplace
Gaps
Questions
| ||
Job Matching/Placement
Need for information on available job opportunities for persons with disabilities
To know about job opportunities
|
| EXISTING RESOURCES | GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|
SG Enable - Job Advisory
|
||
SG Enable — Disability Employment Jobs Portal
|
Jobs listed on most job portals do not reflect if the hiring company is interested to employ PWDs. Career events are not always universally designed as well. | Employers can reflect if they are keen to employ PWDs, at career events, on job portals and other avenues.
Having a “ready-to-hire PWDs” mark would ease PWDs’ job search process. |
ABLE Return to Work Programme
|
||
BizLink Vocational Assessment Service
|
||
SPD Employment Support Programme (ESP)
|
||
SPD Transition To Employment Programme (TTE)
|
||
ARC Employability & Employment Centre (E2C) Programme
|
||
| MINDS Employment Development Centres (EDCs)
Provides vocational training for adults with intellectual disabilities aged 18 and above: |
||
Gaps
Questions
| ||
Continuing Career Development
Need for continued opportunities for job growth, career development and skills upgrading
| EXISTING RESOURCES | GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|
SG Enable
|
Questions:
|
Consider availing using HDB void decks or unwanted public buildings as training venues. |
Workfare Training Support (WTS) Scheme
|
Even with the WTS Scheme, accessing SkillsFuture training courses remain difficult for some. A blind individual with a Master’s degree in counselling called SG Enable asking for help to navigate available subsidies for training such as the WTS, but she was offered Sheltered Workshop training instead. | |
SkillsFuture
|
The SkillsFuture platform is difficult to navigate for the blind. | To facilitate lifelong learning, have additional funds for the SkillsFuture Credit of PWDs. |
Gaps
| ||
Need for financial independence and stability
| EXISTING RESOURCES | GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|
Workfare Income Supplement
|
||
Handicapped Earned Income Relief (EIR)
|
PWD Training & Work Readiness
Need to be job ready
How 'job ready' is understood
|
| EXISTING RESOURCES | GAPS AND THEIR CAUSES | POSSIBLE SOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|
SkillsFuture
|
||
| Vocational Training in SPED Schools | ||
School-to-Work Transition Programme (S2W)
|
| |
| Framework for Vocational Education
To guide the 19 SPED schools in designing a structured vocational education programme that includes vocational guidance, an assessment of students’ interests, preferences and strengths, and opportunities for structured and authentic work experiences to support development of work habits and skills. Enabling Masterplan 3[59]
|
Some SPED students have difficulty mastering job skills training even when approaching graduation/18 years old. Can they continue learning even after graduation? | Allow SPED students to attend courses ad-hoc, even after graduation. |
| SPED school graduates lack internship opportunities during their school-going years and a foothold in permanent employment. SPED schools and VWOs typically do this through their own contacts. | Have a central coordinator that facilitates the internship process. What are the possible alternatives for students who are unsuccessful in an internship placement? | |
| Content taught in WSQ- and WPLN- certified courses may not always be understood, and skills learnt not retained and applied. | ||
| Transition Planning Guide
(entitled Transition Planning For Living, Learning And Working - Making It Happen)
|
Question: Are there channels available for teachers and parents to provide feedback on the transition planning process? | |
| Metta School’s Vocational Certification Programme
Institute of Technical Education Skills Certificate (ISC)
|
||
Metta School’s Employment Pathway Programme (EPP)
|
||
Metta School’s C (Career) Programme
|
||
APSN Delta Senior School’s Vocational Certification Programme - Singapore Workforce Skills Qualifications (WSQ)
|
||
| Students in Institutes of Higher Learning (IHL) – Universities or Polytechnics | ||
IHL Internship Programme
|
||
Rise Mentorship Programme
|
||
| Non-Students/Adults with Disabilities | ||
| Vocational Training
For post-primary school students, available at:
|
||
BizLink Vocational Assessment Service
|
||
CV Clinics by Singapore Business Network on Disability
|
||
Training Programmes
|
||
ABLE Return-to-Work Programme
|
||
Hospital-to-Work Programme
|
||
SPD Employment Support Programme (ESP)
|
||
SPD Transition To Employment Programme (TTE)
|
Job coaches face difficulties in providing psychosocial support for those with acquired disabilities. Some PWDs have difficulty accepting their disabilities and the job coaches are not trained to provide psychosocial support to address these issues. | |
Employability & Employment Centre (E2C) Programme
|
An individual with autism received vocational assistance from ARC; he paid $494 (after subsidy) for the vocational assessment but was deemed unemployable. However, he managed to secure a job later through his & his family’s efforts with Dignity Kitchen.
|
|
| MINDS Employment Development Centres (EDCs)
Provides vocational training for adults with intellectual disabilities aged 18 and above:
|
||
Sheltered Workshops
|
||
Gaps
Questions
| ||
- ↑ https://www.straitstimes.com/singapore/aged-and-disabled-should-be-top-issues-in-the-workplace-survey-of-hr-leaders-show
- ↑ https://www.msf.gov.sg/media-room/Pages/Employment-rate-of-Persons-with-Disabilities.aspx
- ↑ https://www.tafep.sg/sites/default/files/E-News%20April%202011_files/Publication%20CIW%20Start%20Up%20Kit%20(as%20of%20040712).pdf
- ↑ https://www.straitstimes.com/lifestyle/myth-of-the-disabled-worker
- ↑ https://www.straitstimes.com/lifestyle/myth-of-the-disabled-worker